Mysterious Methane Plumes Spotted Above Texas Oil and Gas Fields
(Bloomberg) -- A satellite spotted two plumes of planet-warming methane rising from a patch of East Texas that's home to multiple oil and gas operations.
State regulators said they couldn’t identify the source of the methane, which is the primary component of natural gas and traps 80 times as much heat than carbon dioxide in its first two decades in the atmosphere. Stemming methane leaks and stopping unnecessary releases is one of the most powerful steps that can be taken to slow global warming.
The two plumes were detected by geoanalytics company Kayrros SAS using a Nov. 29 satellite observation from the European Space Agency. Kayrros estimated that the plumes originated from different sources east of Dallas, about 15 miles apart, in an area dotted with fossil fuel infrastructure.
The plumes had estimated release rates of 21 tons per hour and 24 tons per hour. It’s not possible to determine the duration of leaks because satellites only capture one moment in time. If they lasted an hour, the two clouds combined would equal the average annual emissions from about 800 cars running in the U.S.
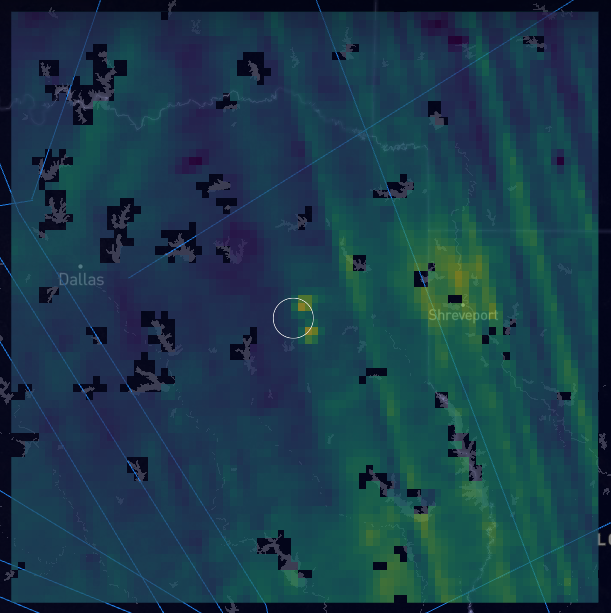
Some methane plumes found by satellites can be tracked to specific sources, especially if a company reveals that it released gas at that location at that time. But without anyone stepping forward, the source of such plumes — where multiple companies are operating in a small area — can remain a mystery. On-the-ground monitoring is also sometimes used to link releases to specific producers.
Companies operating pipelines nearby include Boardwalk Pipelines LP, Enbridge Inc. and Atmos Energy Corp. Boardwalk said it didn’t have any leaks or releases that could have caused the clouds. An Enbridge representative said the company isn’t aware of any such release. Atmos didn’t respond to multiple requests for comment.
Texas regulators also weren’t able to identify the source of the methane plumes. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality wasn’t aware of the plumes, a representative said. A spokesperson for the Railroad Commission of Texas, the primary state regulator of the oil and natural gas industry, referred questions to the TCEQ.
More stories like this are available on bloomberg.com
©2021 Bloomberg L.P.
KEEPING THE ENERGY INDUSTRY CONNECTED
Subscribe to our newsletter and get the best of Energy Connects directly to your inbox each week.
By subscribing, you agree to the processing of your personal data by dmg events as described in the Privacy Policy.
More gas & LNG news

Arctic Weather Blast to Put Strain on Europe’s Energy Systems

UK Carbon Prices Surge as Minister Talks About EU Market Linkage

TotalEnergies’ Mozambique LNG Poised for Decision on $4.7 Billion US Loan

European Gas Prices Pare Gain on Russia-Ukraine Truce Hopes

EU Leaders Call for Ukraine Gas Solution on Slovakia’s Push

UAE’s Adnoc Seeks Deals for Gas Fields in Major US Push

Goldman Wins Rare Solo Role on Blockbuster $19 Billion Deal

EU to Ease Gas Storage Requirements to Avoid Price Spikes

Equinor reveals promising gas discovery in the Norwegian Sea
















