Fashion Is the Next Frontier for Clean Tech as Textile Waste Mounts
(Bloomberg) -- The $1.7 trillion fashion industry is a major polluter: By one estimate, it’s responsible for between 8% and 10% of annual greenhouse gas emissions, more than aviation and shipping combined. Clothes manufacturing relies on fossil-fuel-derived fibers like polyester and guzzles energy and water. And the churn of fast fashion means that many items are discarded soon after they’re purchased, which has contributed to eye-popping amounts of textile waste.
Two textile-focused startups are among this year’s BloombergNEF Pioneers award winners: Circ, in Danville, Virginia, turns mixed-fiber fabric back into its reusable raw materials, while Paris-based EverDye has developed a lower-impact textile dyeing process.
Much of the fabric produced today is a blend of cotton and polyester, which is more durable than pure cotton. But the blended fibers are extremely difficult to separate and therefore challenging to recycle.
“It’s so hard to mechanically separate them. You can’t comb it apart,” says Sonja Salmon, a textile science professor at North Carolina State University. “A machine will think it’s the same thing.”

That’s why Circ turned to chemistry instead. Its technology uses water as a solvent, plus pressure, to break down large polyester molecules — polymers — into their building blocks, or monomers, says Peter Majeranowski, the company’s president. This helps separate the two types of fiber. Circ then purifies the polyester monomers and the cotton so they can both be reused in textile production.
The startup has spent significant time “refining and developing our process to ensure that our materials are better than virgin, from a greenhouse impact,” says Majeranowski.
In addition to venture and supply chain investment, Circ has received investment from Patagonia, Inditex (Zara’s parent company) and the European fashion platform Zalando SE. The company would like brands to sign multi-year contracts to use material recycled with its technology. But making commitments for several seasons is uncommon in the industry, Majeranowski says — “a muscle that brands aren’t used to.”
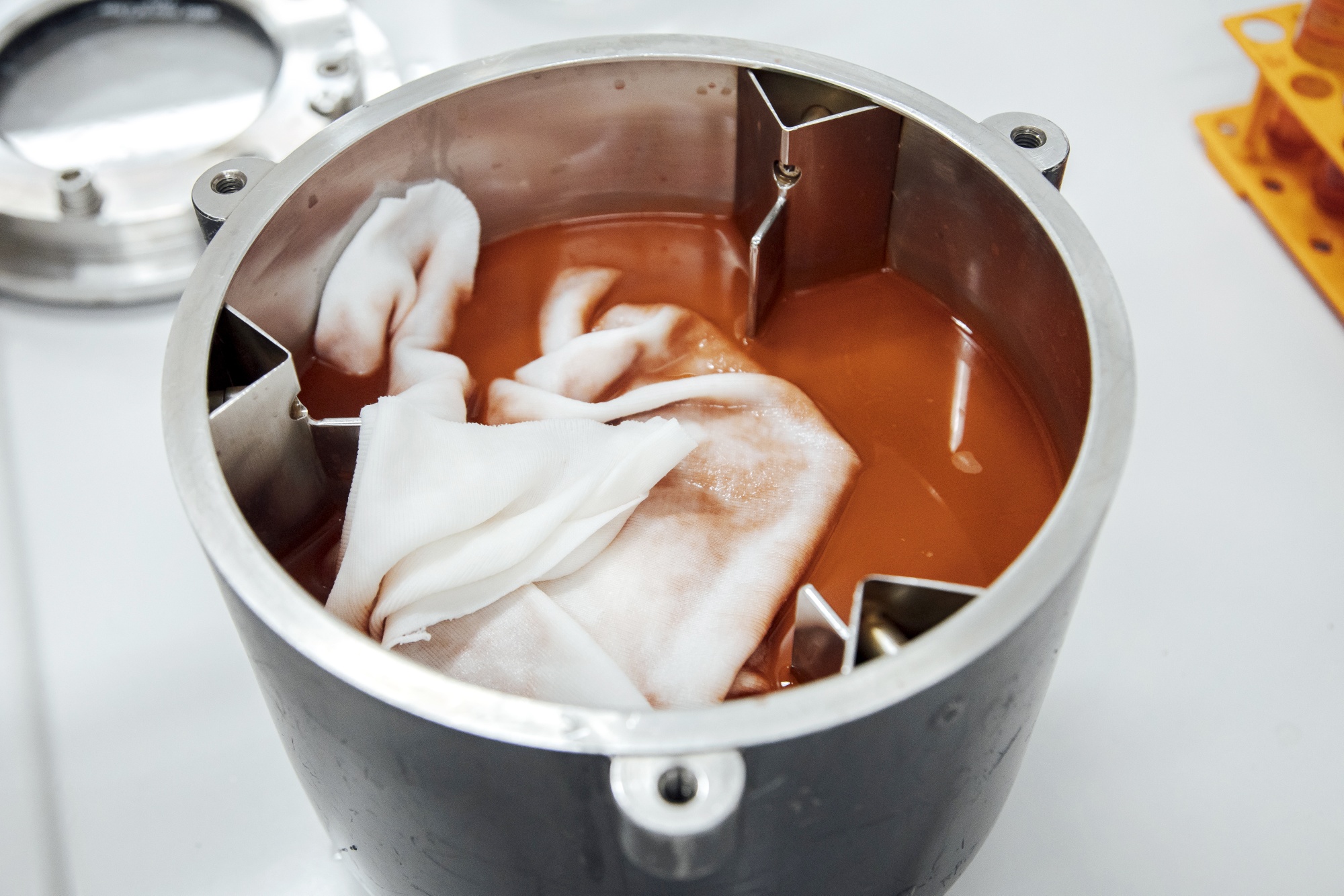
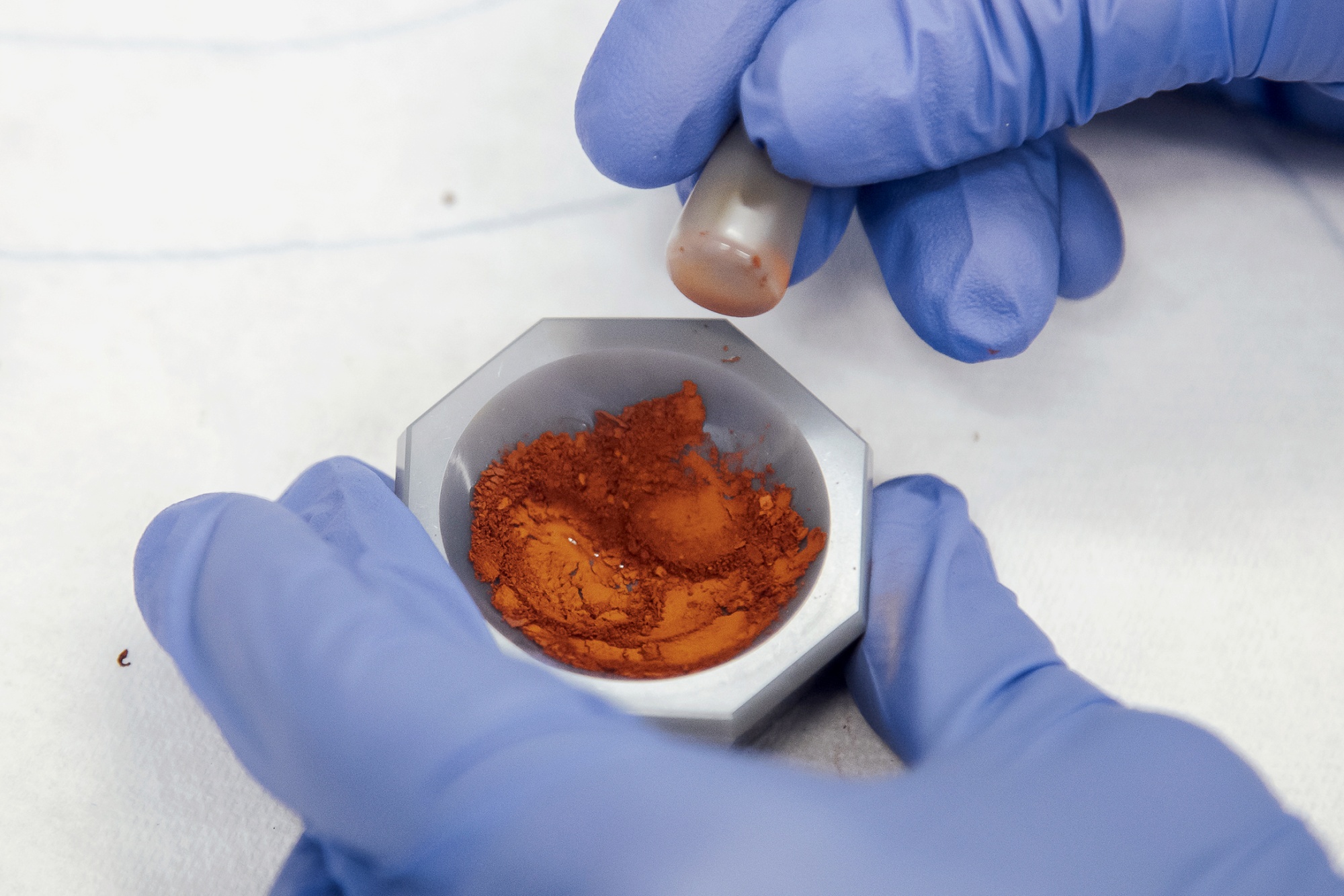


Dyeing the fabric that gets sewn into garments is an energy-intensive step in the manufacturing process. Conventionally, pigments are heated to very high temperatures so that the color can bind. EverDye says it’s found a way to do this with room-temperature water.
Mineral pigments used for textiles are generally negatively charged, says Christelle Chauffeton, a research scientist at EverDye. The fabric is also negatively charged, so the two have no affinity and the color won’t adhere. That’s why the dyeing process typically relies on additives, binders and high heat.
EverDye takes mineral pigment and “synthesizes it directly on a nanoparticle of biopolymer,” says Chauffeton, that was chemically modified to be positively charged. When the biopolymer (or natural polymer) is put next to a negatively charged fabric, the pigment will go on the fabric without additives or the need for intense heat. Later, another application of heat causes the nanoparticles to come together and form a film on the surface of the fibers, trapping the pigment.
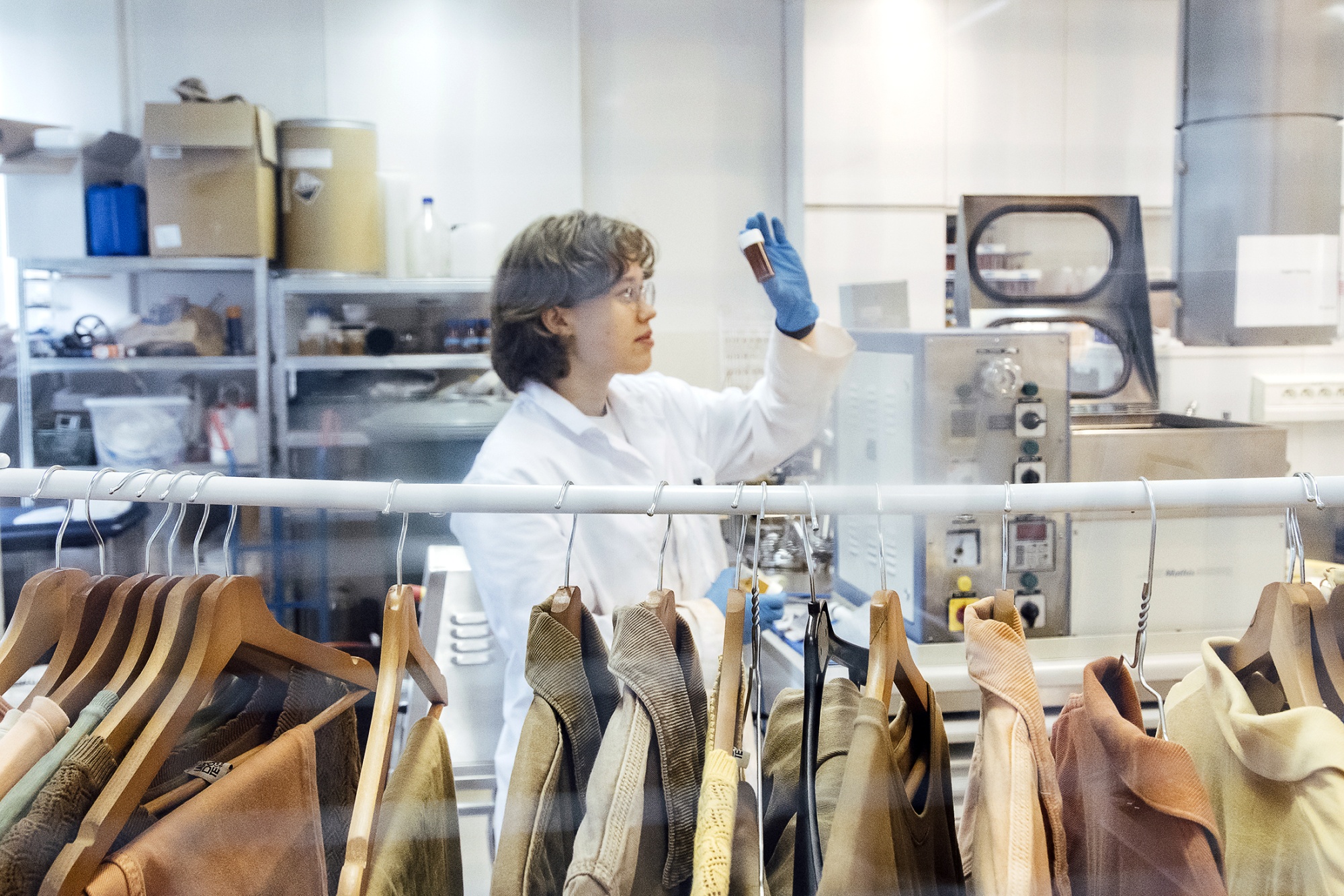


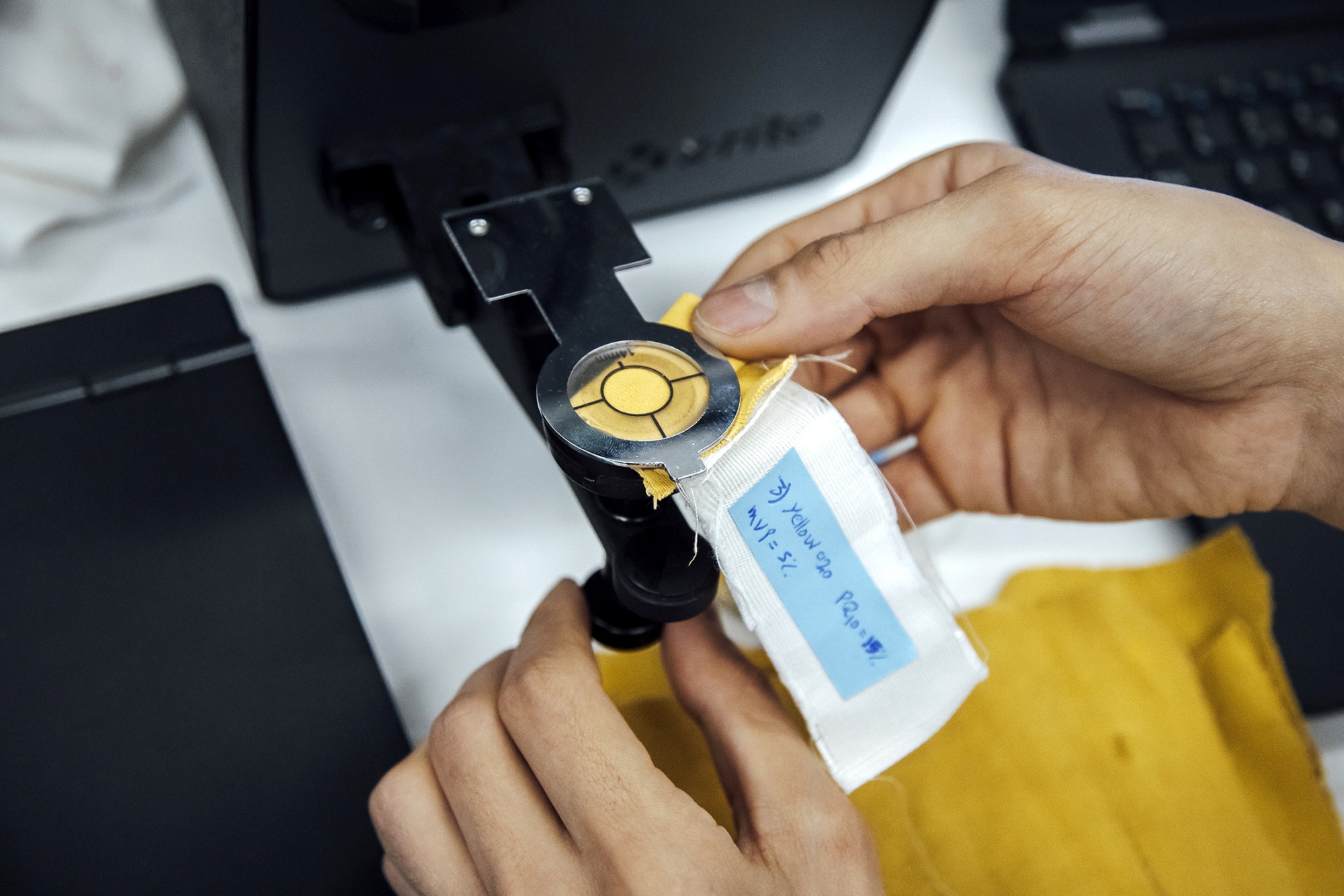
The startup can now dye fabrics brown, orange or yellow and is fine-tuning its approach to create blue, red and black hues. “It takes time to adapt the formulas,” says Victor Durand, EverDye’s head of operations.
It launched a small capsule collection last October and is doing pilot testing with brands including Lacoste and Petit Bateau. The company is currently raising money for its series A funding round.
“Our goal is to be a regular provider of dyes in the supply chain,” Durand says.
EverDye and Circ join a host of firms innovating in pursuit of lower-impact textiles, such as Boston-based Galy, which grows cotton in a lab to reduce the crop’s heavy water and fertilizer use, and Algaeing, an Israeli startup that makes biodegradable yarns and dyes out of algae.
Buying clothing secondhand — or just buying less of it — is an effective way to shrink fashion’s footprint. But the global business of making new garments isn’t going away anytime soon. Circ, EverDye and their peers are working to clean up the process step by step.
- How 12 Climate Tech Startups Are Shaping the Energy Transition in a Turbulent World
- An Iconic Brewery is Installing a Giant Heat Pump to Clean Up Its Emissions
- Why Homeowners Choose Heat Batteries Over Heat Pumps
©2025 Bloomberg L.P.
KEEPING THE ENERGY INDUSTRY CONNECTED
Subscribe to our newsletter and get the best of Energy Connects directly to your inbox each week.
By subscribing, you agree to the processing of your personal data by dmg events as described in the Privacy Policy.
More renewables news

US Green Steel Startup Raises $129 Million Amid Trump Tariff Uncertainty

Spain Signals Openness to Keeping Nuclear Power Plants Open

Musk Foundation-Backed XPRIZE Awards $100 Million for Carbon Removal

As Tesla Falters, These New EVs Are Picking Up the Pace

Nissan Commits Another $1.4 Billion to China With EVs in Focus

NextEra Energy reports 9% rise in adjusted earnings for Q1 2025 as solar and storage backlog grows

US Imposes Tariffs Up to 3,521% on Asian Solar Imports

India Battery-Swapping Boom Hinges on Deliveries and Rickshaws

China Reining In Smart Driving Tech Weeks After Fatal Crash
















